It is a dynamic model of learning and group dynamics. Schein’s model of organizational culture is a framework explaining the impact of company culture on an organization with a focus on learning and group dynamics.
PPT Schein’s Model of Organizational Culture PowerPoint Presentation
There are also deeper layers which provide a much greater insight into what a.
Schein model of organizational culture examples. To illustrate, it is a little. Each of these is described in detail in this section. Surely, a transformation will fail if it is not consistent with the organization culture.
Examples of this would be employee professionalism, or a family first mantra. Edgar schein‘s model of organizational culture originated in the 1980s. As more investigators and theoreticians have begun to examine organizational culture, the normative thrust has been balanced by more descriptive and clinical research ( barley, 1983 ;
It discusses three central elements related to organizational culture. Edgar henry schein identified three distinct levels in organizational cultures: The framework of this study will be guided by the following factors.
How space is owned and allocated, and what it means to people. What kind of offices and layout is used; As an example, novonordisk claims that it has a creative and supportive culture which motivates its employees to be the best they can.
They learn from their past experiences and start implementing practices, and collectively the employee's attitudes form the culture within the organisation. It is the culture of the workplace which decides the way individuals interact with each other and behave with people. The schein's model of organizational culture is a method which aims at explaining the concept of culture and the way it affects organizations.
There are shallow layers that have some impact on an organizations culture or which may be some indication of what a culture is actually like. They can be seen, heard and felt. The reengineering alternative by william schneider.
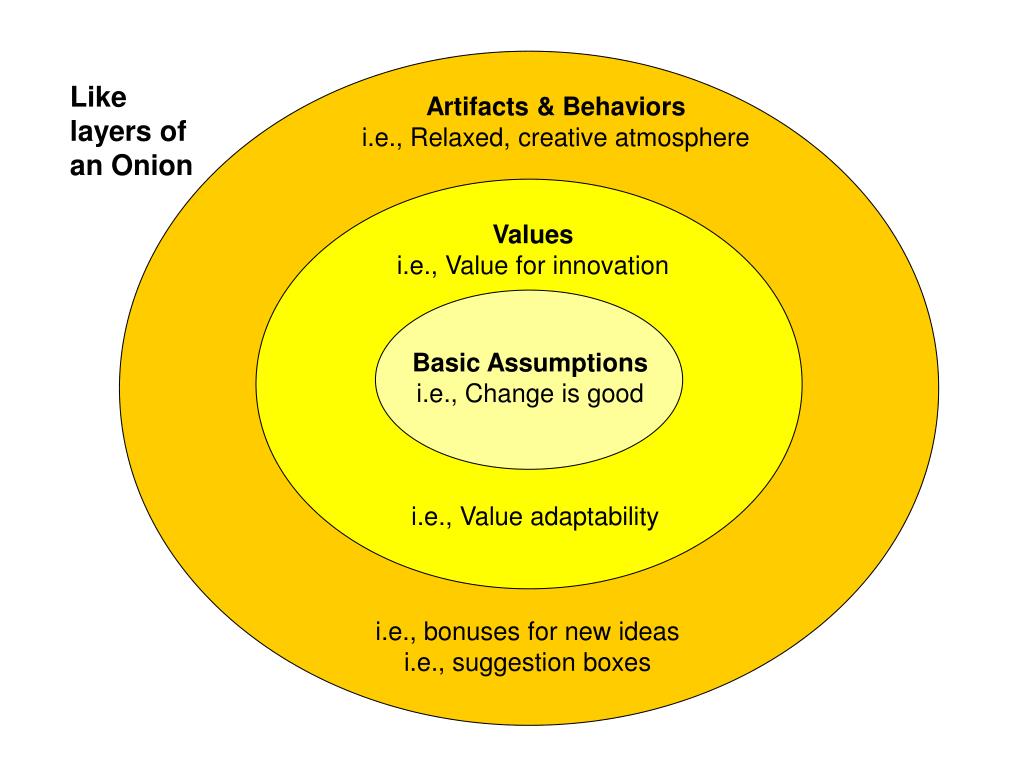
Artifacts are the visible signs of an organisation's culture. The model put forward by schein defines organizational culture as follows: Schein (2004) identifies three distinct levels in organizational cultures:
Proposes that the structure of organizational culture could best be thought of as consisting of different layers, as represented in figure 1. The principles, ideologies as well as policies followed by an organization form its culture. It is also interesting that she develops her own model out of his initial thinking.
Schein is a former professor of mit sloan school of management, known for his remarkable work in the fields of organizational development and organizational culture. Schein (2004) argues that there are three major levels to consider when analysing culture: Schein's model of organizational culture originated in the 1980s.
How the organizational culture framework defines culture in three levels. (1) observable artifacts of culture; Edgar schein’s organizational culture triangle says that there are different layers to the cultures within organizations.
These are the “visible” symbols of the culture. Edgar henry schein (born march 5, 1928), a former professor at the mit sloan school of management, is known for his work in the field of organizational development, more so in areas such as career development, talent management, group dynamics and cultural developments. The levels of organisational culture and relationship between them.
Trouble may arise if espoused values by leaders are not in line with the general. Artefacts are the surface level of an organisational. The term “organization culture” refers to the values and beliefs of an organization.
Structural model of culture indicating different levels of culture. Wilkins & ouchi, 1983 ). Organizational culture and leadership (3rd ed.).
Edgar schein ‘s model of organizational culture originated in the 1980s. Edgar schein believed that organisations take time to develop a culture as the employees go through various changes and adapt to the external environment and solve organisational problems. According to schein 1905, organisational culture has three levels:
Schein’s definition of organisational culture. Schein describes the organizational culture over 3 levels: Levels of effectiveness, and the concept of organizational culture has served this purpose well (e.g., o’toole, 1979 ;
Edgar schein’s model is one of the most cited models of organizational culture. The ‘truth’ and how it is determined. You may recall from reading hatch that she categorizes schein in the modernist camp.
In simple words, organizational culture could be thoughts of as an organization’s way to success. He proposed three distinct levels in organizational cultures: Artifacts and behaviors, espoused values, and assumptions, which came to be known as edgar.
These are the symbols of culture in the physical and social work environment. Cultural concepts can move between these two layers over time and are associated with different levels of awareness within the organization. Artifacts, espoused beliefs and values, and at last, basic underlying assumptions.
Culture is what a group learns over a period of time as that group solves its problems of survival in an external environment and. These are visible accessible and tangible. Schein’s model of organizational culture was developed in 1980 by edgar schein, then sloan professor emeritus at the sloan school of management at mit.
Schein (1985) described six types of assumptions that form what johnson and scholes would describe as the paradigm for an organization. Edgar schein identified a model of an organizational culture where the basic assumptions shape values and the values shape practices and behavior, which is the visible part of the culture. Edgar schein model of organization culture.
For example, what the dress code is; Artifacts and behaviors, espoused values. How employees address each other and how they communicate internally and externally.
Often shown as a pyramid, schein’s original model was presented as three different layers. In this paper, i describe schein’s (2004) basic tenets of organizational culture and leadership and examine the different types of organizational assumptions explored by schein.
Edgar schein made a notable mark on the field of organizational development. These are the “visible” symbols of the culture.

Integrated Leaders Design Your Organization’s Culture
“the only thing of real importance that leaders do is to create and manage culture.

Schein iceberg model of culture. Three key features of the iceberg model: Edgar henry schein (born march 5, 1928), a former professor at the mit sloan school of management, is known for his work in the field of organizational development, more so in areas such as career development, talent management, group dynamics and cultural developments. Edgar schein, grandfather of the study of organizational culture, introduced the iceberg model as a way of visualizing some key cultural features.
Edgar schein is a former professor at the mit sloan school of management in massachusetts, usa. They gain from their past experiences and start practicing it everyday thus. Nevertheless, despite wide scholarly adoption of schein's model of organizational culture, sociologist aviad raz (2006), raised two problems on the.
Edgar schein model of organization culture. Artifacts (the surface manifestations of culture), values, and assumptions. The deeper the layer, the harder it becomes to adjust it.
Edgar schein’s model of organizational culture. Organizations do not adopt a culture in a single day and in fact learn from past experiences and start practicing it every day thus forming. Strategy, leadership, and culture are the three fundamental pillars that define the success of any organization.
Organizational culture in terms of the functions it carries out in the organization’.124 In the article of “coming to a new awareness of organizational culture”, schein (1984) identified three distinct levels in organizational culture as artifacts & creations, values and basic assumptions. Some of an organization’s culture is visible at first sight, but much of it is below the waterline, and out of sight.
Schein (2004) argues that there are three major levels to consider when analysing culture: As has been stated, for schein the function of organisational culture is to solve the problems organisations have of external adaptation and internal integration.122 this is an example of a ‘functionalist perspective’,123 meaning the theorist ‘views. Download scientific diagram | the iceberg model of organisational culture.
The model is also called the edgar schein iceberg model. Schein model focus on building general cultural framework rather than defining cultures into specific types, although it provides a deep insight into organizational culture, due to lack of phyletic classification like hofstede model or cameron and quinn model which can describe the concrete types and carry out comparative work between different. Schein artifact values of organizational culture
Based on a conceptualisation by sackmann, s. Artifacts, espoused beliefs and values, and at last, basic underlying assumptions. Schein’s iceberg model (schein, 1992) is useful in that it illustrates that some cultural aspects of an organisation are visible while some are hidden and difficult for outsiders or even new members of an organisation to interpret.
Visible, surface elements of an organization’s culture, that an outsider would notice. Also referred to as edgar schein onion model because it looks like a bulb onion. Schein’s model of organizational culture is a framework explaining the impact of company culture on an organization with a focus on learning and group dynamics.
Edgar schein is well known for his ground breaking work on the organizational culture model and divided the organizational culture into three different levels. Often, up to 90% of an iceberg’s actual area remains hidden underwater. Cultural concepts can move between these two layers over time and are associated with different levels of awareness within the organization.
Edgar schein proposed a model of an organizational culture where the basic assumptions shape values and the values shape practices and behavior, which is the visible part of the culture. Like an iceberg, the lower part is hidden; Also, he has worked for many years as a consultant in organis.
Schein’s model of organizational culture was developed in 1980 by edgar schein, then sloan professor emeritus at the sloan school of management at mit. Employees will act and behave in the desired manner when. Edgar schein analyzed organizational culture into three distinct levels:
The term ‘iceberg model of culture’ is inspired by the icebergs found in polar seas. Edgar schein‘s model of organizational culture originated in the 1980s. Schein describes the organizational culture over 3 levels:
Examples of visible cultural aspects include. First dimension in schein’s (1984) organizational culture model consists of visible and observable elements such as. Only approximately 10% is visible above the water surface.
Edgar schein iceberg model or edgar schein onion model. They are kind of like an iceberg, with the most important elements most hidden from view. Similarly, culture and behaviors have both visible and invisible components.
Understand the iceberg model of culture more clearly and learn every aspect of the surface culture and the larger deep culture to drive organizational success. In practice, the three levels of schein’s model of organizational culture are sometimes represented as an onion model as it is based on different layers. Cultures are deep seated, pervasive and complex.
To illustrate, it is a little bit like an iceberg with some levels visible, some others partially or not visible. February 1990 abstract the concept of organizational culture has received increasing attention. Yet, according to edgard schein, organizational learning, development, and planned change cannot be understood without considering culture as the primary source of resistance to change. and the bottom line for leaders is that if they do not become conscious.
Figure 6 schein’s iceberg model of culture. Deeply embedded in the core of the onion we find the assumptions. The levels of organisational culture and relationship between them.
An iceberg has visible parts on the surface of the water and invisible parts that are underwater. Schein’s definition of organisational culture. How the organizational culture framework defines culture in three levels.
Often shown as a pyramid, schein’s original model was presented as three different layers. Intercultural competence knowledge of theories and concepts of power relations refers to mechanisms dealing with power within and between groups show a willingness and ability to look at culture, identity and related aspects. The outer layer is fairly easy to adapt and easy to change.
Artefacts are the surface level of an organisational.
This management theory says that leadership effectiveness is a type of element of two factors: Dunphy and stace (1993), put forth a situational or contingency model of change, which emphasized on the fact that organizations should vary.
Situational (Contingency) Approaches to Leadership Principles of
In the case of other theories of management if the manager has failed to achieve the goal due to factors which are beyond the control of the manger than also he or she faces the consequences but since this theory acknowledges the fact that business is filled with contingencies there is this scope of a good manager being retained in.
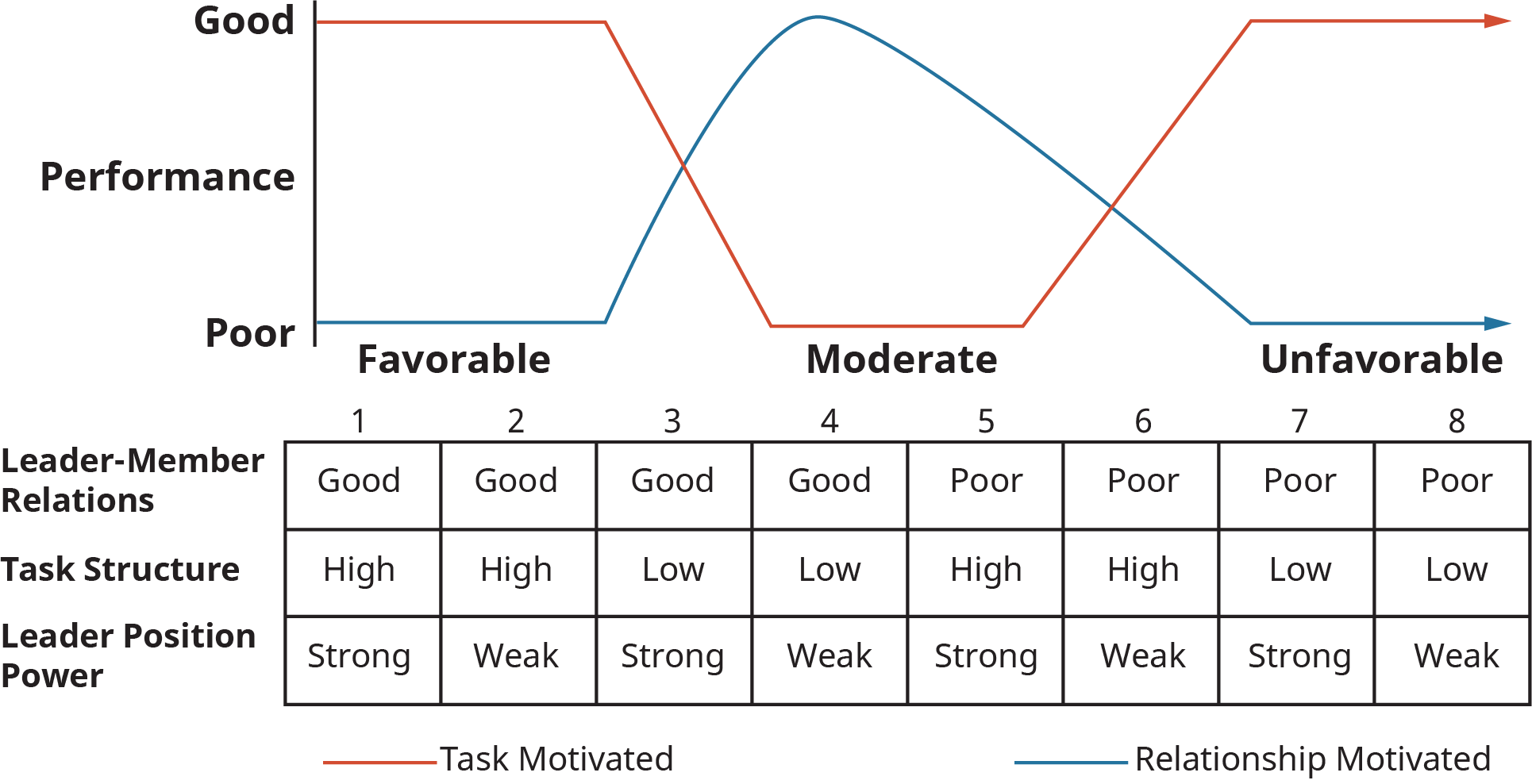
Contingency model of management. You generally evaluate relation motivation or task motivation, by the lpc scale. This model contains the relationship between leadership style and the. This article consolidates the maturation.
It gives no one path of management. According to the fiedler model. Or get a text to speak with a treatment support advisor today.
Contingency management is a highly effective treatment for substance use and related disorders. It then details areas in which. Applying the fiedler contingency model step 1:
However, few psychiatrists are familiar with this intervention or its application to a range of patient behaviours. In addiction treatment programs, this kind of reward or incentive is called contingency management (cm). Fiedler’s contingency theory of leadership effectiveness was based on studies of a wide range of group effectiveness, and concentrated on the relationship between leadership and organizational performance.
While some theories from the early twentieth century like max weber’s principles of bureaucracy emphasize standardization and process, contingency theory looks closer at how leadership. Dunphy and stace (1993), put forth a situational or contingency model of change, which emphasized on the fact that organizations should vary. Relation motivation/ task motivation, and circumstances.
Fiedler’s contingency theory of leadership says that a leader must be able to identify which management style will help. In the fiedler contingency model, leadership styles are fixed and unchangeable. Applying the contingency theory of management requires.
The contingency model is an extended version of lewin’s three step in which dunphy and stace (1988, 1992 and 1993), explained the process of change from the transformational organization perspective. Fred fiedler's contingency model focused on a contingency model of leadership in organizations. It is comprised of a broad group of behavioral interventions that provide or withhold rewards and negative consequences quickly in response to.
The contingency theory is a set of behavioural theories that can be used to forecast organizational behaviour. Certain factors come into play that define whether a particular leader or leadership style will be effective for the given situation. Fred fielder developed one of the first contingency theories called fiedler’s contingency theory of leadership.
It considers the nature of the work of the organization and the approach of the workers. In this article, we define the contingency theory of leadership and examine three specific models for how it can be applied in a work environment. The contingency theory definition offers a dynamic approach to leadership.
This paper describes contingency management and evidence of its efficacy for reducing drug use. The contingency management approach was developed by management psychologist named fred fielder. We asked clinicians at the hazelden betty ford foundation to explain.
The theory integrates various management approaches. Instead, a leader should be appointed who can make decisions based on the situation and relative conditions. This theory was made popular by fred.
The contingency theory of strategic conflict management, which began as an elaboration, qualification, and extension of the value of symmetry propounded in the excellence theory, has, over the last decade, come into its own and emerged as an empirically tested perspective. It proposes that there is no one best way to organize or lead a company. The contingency models have similarities but have their distinct views on leadership.
The contingency theory of leadership focuses on how specific situations affect a leader’s effectiveness and how a leader’s ability to adapt can be their most important tool in the workplace. The contingency theory approach is practical when integrated into organizational theory. Different types or specifics of organizations are needed in different types of environments;
One can acquire important insights on leadership techniques by using contingency thinking. The contingency model is an extended version of lewin’s three step in which dunphy and stace (1988, 1992 and 1993), explained the process of change from the transformational organization perspective. Achieve the organization’s goals in a particular situation.
Several models attempt to understand the relationship between style and situation. With the help of such a theory, the management can decide the best way to lead the organization and make the right decisions. Management must be concerned, above all else, with achieving alignments and good fits;
The contingency approach to management finds its foundation in the contingency theory of leadership effectiveness developed by management psychologist fred fielder. Contingency theory of management (ctm) has been used in multiple research approaches, both qualitatively and in mixed methods approach to help in understanding leadership situations and interactions between managers and employees— employers and employees. Those factors include the task, the personality of the leader and the composition of.
The contingency theory of leadership puts forth the idea that the success of a leader hinges on the specific situation at hand. Identify your leadership style think about the person who you've least enjoyed working with, either now or in. Fiedler’s contingency theory is one of the first formalized management theories to demonstrate the importance of selecting leaders based on group goals and dynamics.
American addiction centers maintains a strong partnership with a large group of insurance companies at our addiction treatment facilities. Identify your situation answer the questions: Contingency theory is a set of behavioural theory which postulates that there is no single way or the best method to organize and lead an organization in a management set up.
This relationship became to be known as the fiedler contingency model. Next, you need to determine the current situation you find yourself in.

Fiedler's Contingency Model Theory Of Leadership
Fiedler’s model is one of many contingency theories that stress.

Fiedler's contingency leadership model determines if a leader's style is. Instead, a leader's effectiveness is based on the situation. Fiedler argues that leaders should take a number of environmental or situational factors into account before deciding on the appropriate leadership style: Leaders would be very unlikely to be successful if they cannot ‘match’ their personal leadership style to the.
This approach emphasizes the importance of situational factors such as the task at hand, the team members, and the environment. Fiedler’s contingency model states that there’s no one best style of leadership. The unique type of leadership will depend on the situation and the life experiences that you have encountered.
The framework argues that there is no one best style of leadership. The premise of fiedler’s contingency model of leadership is that a person’s leadership style is determined by the person’s life experiences and cannot be changed. Extensive research conducted in the following decades showed that people, though influenced by previous experiences, are not.
The fiedler’s contingency model of leadership. Fiedler’s contingency model of leadership is a business framework that evaluates the effectiveness of a leader in an organization. Instead, a leader’s effectiveness is determined by whether the leader’s style and the environment in which the leader is performing complement each other.
Fiedler’s contingency theory of leadership has three main contingency variables: The contingency approach to leadership suggests that there is no one best way to lead and that the most effective approach to leadership depends on the situation. The fiedler contingency model developed by fred e fiedler is a behavioral theory that leadership style effectiveness varies by situations.
The first variable, leadership style, is how a leader behaves toward subordinates under specific situational conditions. The level of clarity, rules, and job descriptions. Explore the main concepts of fiedler’s contingency model, including determining a leader's style and situational control.
You prioritize performance, structures, plans and schedules to get things done. Rather, the most effective leadership style for any given situation is one that aligns with the situation at hand. This is the first component in fiedler’s model.
In order to assess a leader’s leadership style, you must first understand how a lpc scale works. Things have changed since then. The theory was developed in the 1960s by austrian psychologist.
The premise for this model is that. Countless situational factors as well as the followers themselves affect a leader’s abilities. What are the two contingency leadership theory leadership styles?
Fiedler's contingency leadership model determines if a leader's style is _____. With the fiedler contingency model, fred fiedler was the precursor of hershey and blanchard’s situational leadership model. Following are a few of the components of fiedler’s model:
In the 1960s, fred fiedler carried out research on the relationship (contingency) between the effectiveness of the leadership style and the situation. Fiedler’s contingency theory is one of the first formalized management theories to demonstrate the importance of selecting leaders based on group goals and dynamics.in fiedler's model, leadership effectiveness is the result of interaction between the style of the leader and the characteristics of the environment in which the leader works. Fiedler’s contingency model of leadership defines three situational dimensions:
Learn about fiedler’s contingency theory. Assess the situation that a leader faces; Understanding the model the model states that there is no one best style of leadership.
Fiedler’s contingency model of leadership states that a leader’s effectiveness is based on the situation. Telling, selling, participating, or delegating e. He determined that effective leadership is based on how well your leadership style matches the situation.
That was the main approach to leadership in the sixties. Trust levels, respect, commitment between leader and follower. Assess a leader’s leadership style;
Match the situation with the leader’s leadership style. Fiedler’s contingency theory, also known as fiedler’s contingency model or fiedler’s theory of leadership, states that there is not one best style of leadership. Fielder’s contingency model also suggests two key leadership styles.
You foster positive relationships with your team, peers and coworkers by encouraging teamwork and collaboration. Some styles of leadership are effective in certain situations, whereas another style is called for in others. Consequently, the successful leadership style is that the leader’s behaviour meets the needs of the group in the situations obtaining in an environmental setting.
Therefore it is to be said that every leader will have a unique model of leadership. The situational variables of fiedler’s contingency model of leadership. Fiedler’s contingency model in sum.
Structure handy's culture harrison's culture model. Cultures do not have to be logical or consistent, in fact they seldom are and can appear quite haphazard and chaotic to the outsider.

Handy's Organisational Culture Model Simplest Explanation Ever YouTube
Power culture suits small organisations where the leader has direct communication with employees.

Organisational culture model by harrison 1993. Speaking about models, as in. Organisational culture also determines organisational behaviour by identifying principal goals, work methods, how members should interact and address each other; The managers in the hotel take nothing to chance and therefore emphasize.
The principles and beliefs of any organization form its culture. Applied strategic planning the consultant’s kit timothy m. Power culture many small enterprises and large conglomerates such display the characteristics of a centralised power culture.
Harrison (1972) presents a model of culture, known as harrison’s model of culture that divides organisational cultures into the four categories: This is the type of organisation controlled by a key central figure, owner or founder. Organisational culture model by harrison (1993) 17 harrison (1993, p 8) states that “though the model is intended to be.
And how to conduct personal relationships (harrison 1993) furthermore, (brown 1998 p. A survey was conducted using the organizational culture questionnaire (ocq) with the approach of harrison (1993), the job involvement scale, psychological meaningfulness and psychological safety scales to determine the relationships between the variables. Factors that contribute to a change of organizational culture.
Harrison (1993,) states that, though the model is intended to be descriptive rather than evaluative, there is a tendency to perceive it in evaluative terms. Developed by renowned training and od experts, the instrument will identify the shared values and beliefs that constitute your organization's culture. A key role of organizational culture is to differentiate the organisation from others and provide a sense of identity for its members.
(1993), organisational culture, blagdon, mendip papers. Using the denison model focussing on four cultural dimensions namely involvement, consistency, adaptability and mission. Typologies of organisational culture these are rough, lecture note summaries only handy reporting the work of harrison, suggests that organisations can be classified under four cultures:
No two organizations can have the same culture and it is essential for the employees to adjust well in their organization’s culture to enjoy their work and stay stress. To highlight the possible gap between the existing and preferred shared values. Within that period the airline was recognized as an exciting place to.
The kit is based on the newly updated applied strategic planning model, which reflects the authors’ extensive. The uniqueness of this study considered that the organizational culture construct with the. A strong culture is one that is internally consistent, is widely shared, and.
In fact, this paper attracted virtually no attention at the time. In role culture organisations formal. It evolved much later into a commercially published instrument for assessing organization culture (harrison and stokes, 1992).
Through an analysis of existing empirical studies and models link with the organizational culture and performance. Harrison (1993) presents a theoretical model for the purpose of diagnosing organisational culture which is adopted in this study. Based on two dimensions, charles handy and roger harrison followed various organisations and examined how power was distributed and the specific levels of cooperation.
As a result, the management becomes the sole source of visionary focus which reduces the overall ability to improve change strategies and creating identity with new propositions for all. Organisational culture and organisational commitment 121 5.7.1.3 hypothesis 2.3: In 1972 harrison (handy 1993) suggests that organisation culture can be classified into four types:
Role, task, power, and person cultures. Organisations with role culture tend to be reliant on formal rules and regulations. The organization culture decides the way employees interact amongst themselves as well as external parties.
Harrison (1993:11) defines organisational culture as the distinctive constellation of beliefs, values, work styles, and relationships that. The power culture, the role culture, the task culture, and the person or support culture. Schein’s model (1985) ryanair was created by tony ryan with the original vision of a low cost airline company.
The organisational culture model presented in figure 2.1 indicates that the four dimensions of culture orientation are measured within two modes of operation, which are formalisation and. 541) indicates, fails to invoke the criticality of extended reference for change agents. For a culture requiring change, this powerful diagnostic tool suggests how to effect that change.
Handy model of organisational culture: The trainer's package contains all the information, guidance, and support materials you'll need. Ryanair’s organizational culture could be discussed using 3 models schein’s model (1985), harrison and stokes (1990) and slocum and hellreigel (2007).