It refers to the value that an individual places on a particular outcome or a strength of an. This means an individual selects a certain behavior over the other behaviors with.
Expectancy violation is a communication theory that tries to explain the perception of people on another’s unexpected behavior.

What is vroom's expectancy theory. 8), vroom asserts, “intensity of work effort depends on the perception that an individual’s effort will result in a desired outcome”. Vroom’s expectancy theory is known as vie theory of motivation. Expectancy is where the employee believes that what is put into the job will make the job better.
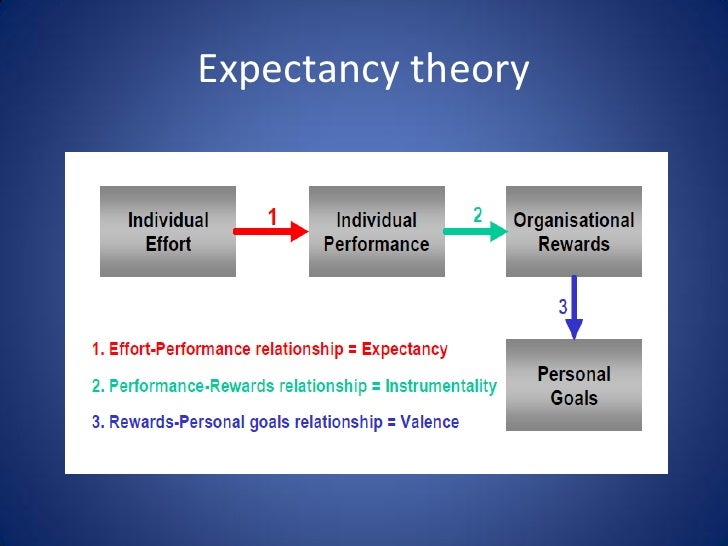
Motivation (force) = ∑valence x expectancy. This is evident by the fact that there have been a very few research studies designed specifically to test vroom’s theory. There is a link between the type and amount of effort invested and the amount and type of reward received.
The algebraic representation of vroom’s expectancy theory is: Vroom’s expectancy theory was originally developed by victor h. In the field of chemistry, valence refers to the attracting or repelling force of an element.
Victor vroom’s expectancy theory is one such management theory focused on motivation. During his academic courses and his career as a professor, victor vroom studied the various factors which affect the performance of an organisation. There is a positive correlation between efforts and performance, the desire to.
“expectancy can be defined as a momentary belief followed by a particular outcome (lee, 2007).”. The expectancy theory was proposed by victor vroom of yale school of management in 1964. If the employee has the desire.
These include efficiency of the performance, leadership, and motivation. First, if they exert enough. (ii) this theory assumes man to be a rational human.
The three elements of the vie theory are: The theory is based on the assumption that our behavior is based on making a conscious choice from a set of possible alternative behaviors. Maslow’s hierarchy of needs and herzberg two factor theory were based on the relationship between internal needs and the resulting effort expended to fulfil them, while.
Similarly, in vroom’s theory, valence refers to the strength of a person’s performance for a. Porter and lawler's expectancy theory: According to the theory, employees are motivated to the extent that their expectations are met in the following ways.
Vroom realized that an employee's performance is based on individuals factors such as personality, skills, knowledge, experience and abilities. Some of the famous motivation theories include the following: This establishes trust and paves the way for the rest of the chain of motivation to succeed.
The theory states that the intensity of a tendency to perform in a particular manner is dependent on the intensity of an expectation that the performance will be followed by a definite outcome and. What are the 5 theories of motivation? (i) vroom’s theory is difficult to research and apply in practice.
He was a canadian professor, and in his entire lifetime, he analysed a variety of factors that impact the organisation's overall performance. Vroom’s expectancy theory is perhaps best suited to the business environment, providing management teams with the vital knowledge that each employee’s motivation is a result of their own perceptions of the link between performance, outcome and reward. Also known as the expectancy theory of motivation, victor harold vroom introduced this theory in 1964.
According to expectancy theory, the behavior we choose will always be the one that. The elements of the expectancy theory are as. According to victor vroom, behaviour is the result of a conscious choice from alternatives.
Abraham maslow postulated that a person will be motivated when his needs are fulfilled. The final process theory of motivation is the expectancy theory of vroom. Vroom stresses and focuses on outcomes, and not on needs unlike maslow and herzberg.
Vroom’s expectancy theory is based on the assumption that an individual’s behavior results from the choices made by him with respect to the alternative course of action, which is related to the psychological events occurring simultaneously with the behavior. The theory also assumes that people are rational and logically calculating. Expectancy theory is a motivation theory first proposed by victor vroom of the yale school of management in 1964.
Vroom in 1964 and extended by porter and lawler in 1968. The theory suggests that although individuals may have different sets of goals, they can be motivated if they believe that: According to him, a person’s motivation towards an action at any time would be determined by an individual’s perception.
This theory can, therefore, be beneficial when creating new motivational strategies within. Vroom’s expectancy theory of motivation. This theory is built around the concept of valence, instrumentality, and expectancy and, therefore, is often called as vie theory.
Victor vroom’s expectancy theory of motivation is a process theory of motivation.it says that an individual’s motivation is affected by their expectations about the future. Expectancy theory was proposed by victor vroom in the 1960s. So, the chain (or equation) of vroom’s expectancy theory is as follows:
Expectancy violation theory is the term used to describe the theory of behavior or action that is either above or beyond the range of what people might normally expect. Specifically, vroom says that an individual’s motivation is affected by how much they value any reward associated with an action (valence), how much. Expectancy theory of motivation was developed by victor h.
Vroom, a canadian psychologist, in 1964. Employees have a preference for getting the most possible joy from their work with little effort. This theory states that individual motivation with regard to the amount of effort expended is a result of a rational calculation.
Vroom’s expectancy theory or expectancy theory of motivation was coined in 1964 by victor harold vroom is a canadian professor of business studies at the yale school of management in connecticut. Individual factors play a large role in the goals that have to be achieved and the behaviour of employees. Vroom suggests that “for a person to be motivated, effort.
Motivational force (mf) = expectancy (e) x instrumentality (i) x valence (v) if either e, i or v are zero, then the equation fails, and this indicates that motivation is low or. Vroom’s model of expectancy theory is based on three parts, expectancy, instrumentality, and valence. Despite these plus points, there are some drawbacks of vroom’s expectancy model as given below:
Vroom’s theory differs from others to some extent, in that it focuses on the here and now as opposed to past behavior.